
Tangent Addition Formula TUTOR TTD
Let's see what the tangent addition formula looks like and solve an example to make it clear. The Tangent function in trigonometry is defined by. \ (\begin {array} {l}tan\;x=\frac {sin\;x} {cos\;x}\end {array} \) . The addition formula for the tangent are achieved from the addition of sine and cosine. To find the addition of a tangent.

Addition Formulae for Tangent. YouTube
To add to the article, the unit circle definitions of the trigonometric function are important namely: sin (theta) = y. cos (theta) = x. tan (theta) = y/x. There are some other memory tricks you can use. Complementary Angle Identities: co is a prefix the stands for complementary. For example in cosine i.e. co-sine.

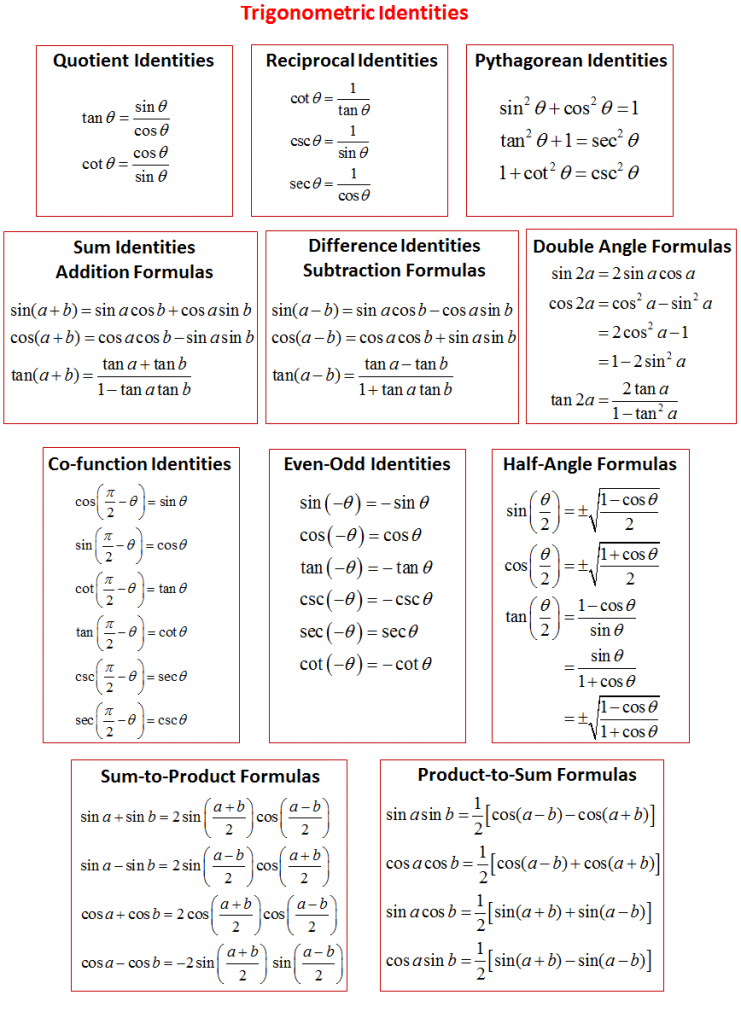
Complete List of Trigonometry Formulas & Identities [Modified]
tangent Sum and Difference Formulas. In this lesson, we want to find a formula that will make computing the tangent of a sum of arguments or a difference of arguments easier. As first, it may seem that you should just add (or subtract) the arguments and take the tangent of the result. However, it's not quite that easy.

Solution. By recognizing the left side of the equation as the result of the difference of angles identity for cosine, we can simplify the equation. sin(x)sin(2x) + cos(x)cos(2x) = √3 2 Apply the difference of angles identity. cos(x − 2x) = √3 2. cos( − x) = √3 2 Use the negative angle identity. cos(x) = √3 2.

Tangent Addition Formula TUTOR TTD
A formula for computing the trigonometric identities for the one-third angle exists, but it requires finding the zeroes of the cubic equation 4x 3 − 3x + d = 0, where is the value of the cosine function at the one-third angle and d is the known value of the cosine function at the full angle.
Trigonometric Functions with Their Formulas
This page titled 8.2: The Tangent Function is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 1.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Dan Sloughter via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request.

Learn how to prove tangent of addition of two angles in trigonometry by using geometry to
In this unit, you'll explore the power and beauty of trigonometric equations and identities, which allow you to express and relate different aspects of triangles, circles, and waves. You'll learn how to use trigonometric functions, their inverses, and various identities to solve and check equations and inequalities, and to model and analyze problems involving periodic motion, sound, light, and.

tangentadditionformula16 TUTOR TTD
Using the cosine angle addition identity. Using the cosine double-angle identity.. sine and tangent are, you can figure them out for the inverse functions! For example, cot(90 + 45) = 1/tan(90 + 45) and so on.. I wanna come up with a formula for tangent of x plus y expressed just in terms of tangent of x and tangent of y. You can view it.

tangentadditionformula4 TUTOR TTD
Cotangent Subtraction Formula. First we note that the cotangent function is odd: Now we can easily derive the cotangent subtraction formula. It is obtained by replacing in the cotangent addition formula: So, we have. In terms of tangents, the cotangent subtraction formula is given by.

Sum and Difference Formulas (With Proofs and Examples) Owlcation
To derive the tangent addition formula, we reduce the problem to use sine and cosine, divide both numerator and denominator by , and simplify. as desired. Double-angle identities. The trigonometric double-angle identities are easily derived from the angle addition formulas by just letting . Doing so yields: Cosine double-angle identity

Trigonometric Addition and Difference Formulas (Identities) Also double angle formulas. hubpages
The Formula: Tangent. The sum and difference angle formula for the tangent function is: Notice the formula has a plus-minus sign and a minus-plus sign. When we are dealing with a sum of two angles, the numerator will contain an addition sign but the denominator will contain a subtraction sign. The opposite is true when we are dealing with a.

Tangent Addition Formula TUTOR TTD
Angle addition formulas express trigonometric functions of sums of angles alpha+/-beta in terms of functions of alpha and beta. The fundamental formulas of angle addition in trigonometry are given by sin (alpha+beta) = sinalphacosbeta+sinbetacosalpha (1) sin (alpha-beta) = sinalphacosbeta-sinbetacosalpha (2) cos (alpha+beta) = cosalphacosbeta.

Tangent Addition Formula TUTOR TTD
The sum and difference formulas for tangent are: tan(α + β) = tanα + tanβ 1 − tanαtanβ. tan(α − β) = tanα − tanβ 1 + tanαtanβ. How to: Given two angles, find the tangent of the sum of the angles. Write the sum formula for tangent. Substitute the given angles into the formula. Simplify.

Tangent Addition Formula TUTOR TTD
Find the tangent of 13pi/12 without a calculator using the tangent angle addition identity. Created by Sal Khan. Questions Tips & Thanks. Want to join the conversation?. and the point (x,y). So, the complete formula would be (y-0)/(x-0)=y/x. So, if you are finding the slope of a line that goes through the origin, all you have to do is take y.

Tangent Addition Formula TUTOR TTD
Tangent Addition Formula. In trigonometry, the tangent addition formula is referred to as the tan (A + B) formula for the compound angle (A+B). It is used when the angle for which the tangent function value is to be determined is supplied as the sum of any two angles. It may alternatively be written as tan (A + B) = sin (A + B)/cos (A + B.

Tangent Addition Formula TUTOR TTD
Tangent Addition Formula - Trigonometric Identities. Calculator ; Formula ; Formula: tan(α + β) = (tanα + tanβ)/(1 - tanα tanβ) Where, tan = Tangent α,β = Angles Related Calculator: Tangent Addition Calculator; Calculators and Converters. ↳ ; Formulas; ↳ ; Trigonometry; Ask a Question . Top Calculators.